Mad about "Mad Cow"
This is a section of a human brain showing spongiform pathology characteristic of Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease.

This is a picture of a "downer cow" with neurologic disease from bovine spongiform encephalopathy ("mad cow").

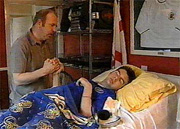
This is a picture of an 18 year old victim of variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (vCJD).
This is an explanation of what Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease from the Creutzfeld-Jakob Disease Foundation:

This is what happened about an equivocal mad cow test in November:

Fortunately Ms. Fong thought it was the duty of the Department of Agriculture to protect the public. What a wild idea!
As reported:
No. Apparently he was "irked". The report continues:

Isn't it time America had a President who defended our interests? Who made sure that the food we ate was safe! That the air we breathe is without pollution! That the water we drink is without contaminants!
It is time for new leadership in Washington! America deserves better!
Bob

This is a picture of a "downer cow" with neurologic disease from bovine spongiform encephalopathy ("mad cow").

This is a picture of an 18 year old victim of variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (vCJD).

This is an explanation of what Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease from the Creutzfeld-Jakob Disease Foundation:
Prion diseases are a group of rare, invariably fatal brain disorders which occur both in humans and certain animals. They first came to public attention in the mid 1980s in the form of the BSE epidemic in the United Kingdom. BSE (bovine spongiform encephalopathy) is a prion disease in cattle. Tissue from infected animals may have contaminated cattle feed, leading to the silent spread of the BSE epidemic. There is also a theory that BSE came from feed contaminated with scrapie, the long established sheep prion disease. Inevitably, concern over whether BSE could pass to humans mounted.This is a picture of our Secretary of Agriculture, Mike Johanns.
In humans the best known of the prion diseases is Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD), which reportedly affects around one person per million per year. In the United States this translates to 250-300 new cases per year. It is well known that CJD is very difficult to diagnose leading to speculation that the one case per million report may be incorrect. Most of the cases are "classical" or "sporadic" CJD (sCJD), occurring for no, as yet, known reason. The sporadic form accounts for approximately 85% of the cases, the familial form approximately 15%. There have also been a few cases which have occurred from contamination via medical procedures; this type is known as iatrogenic or Acquired CJD. Finally over the last few years, another type of Acquired CJD called variant (vCJD) has been identified in young people. vCJD has been linked to ingestion of beef tainted with BSE (bovine spongiform encephalopathy), most cases have occurred in the United Kingdom.

This is what happened about an equivocal mad cow test in November:
A third and more sophisticated test on the beef cow suspected of having mad cow disease would have helped resolve conflicting results from two initial screenings, but the U.S. refused to perform it in November.This is a picture of Phyllis Fong, the Inspector General of the Department of Agriculture.
That additional test, ordered up by the Agriculture Department's internal watchdog, ended up detecting mad cow - a finding that was confirmed on Friday by the world's pre-eminent lab, in England.

Fortunately Ms. Fong thought it was the duty of the Department of Agriculture to protect the public. What a wild idea!
As reported:
Troubled by the conflicting test results, the department's inspector general, Phyllis Fong, ordered the Western blot test this month. By the time an aide notified Agriculture Secretary Mike Johanns, the testing was under way.And was Secretary Johanns happy about what Ms. Fong's action? Did he commend her and thank her for protecting the American public?
No. Apparently he was "irked". The report continues:
Johanns, amid an uproar from the cattle industry, was irked that she did so without his knowledge or consent.Even though
"From my standpoint, I believe I was put there to operate the department and was very disappointed," he told reporters Friday morning.
Consumer groups and scientists urged the department to perform a Western blot test and seek confirmation from the lab in Weybridge, England.This is a picture of the President who put this team together:
In a letter to Consumers Union last March, the department said there was no need for the British lab to confirm the results and that the Western blot test would not have given a more accurate reading.
"We are confident in the expertise of USDA's laboratory technicians in conducting BSE testing," wrote Jere Dick, an associate deputy administrator. Mad cow disease is medically known as bovine spongiform encephalopathy, or BSE.

Isn't it time America had a President who defended our interests? Who made sure that the food we ate was safe! That the air we breathe is without pollution! That the water we drink is without contaminants!
It is time for new leadership in Washington! America deserves better!
Bob













1 Comments:
JOHANNS MUST BE FIRED FOR HIS FAILED RESPONSE TO MAD COW DISEASE IN THE USA, he is responsible for exposing millions to the mad cow agent, whether it be BSE or BASE, both of which have been here for eons. ...TSS
Volume 12, Number 12–December 2006
PERSPECTIVE
On the Question of Sporadic
or Atypical Bovine SpongiformEncephalopathy and
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
Paul Brown,* Lisa M. McShane,† Gianluigi Zanusso,‡ and Linda Detwiler§
Strategies to investigate the possible existence of sporadic
bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) require
systematic testing programs to identify cases in countries
considered to have little or no risk for orally acquired disease,
or to detect a stable occurrence of atypical cases in
countries in which orally acquired disease is disappearing.
To achieve 95% statistical confidence that the prevalence
of sporadic BSE is no greater than 1 per million (i.e., the
annual incidence of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
[CJD] in humans) would require negative tests in 3 million
randomly selected older cattle. A link between BSE and
sporadic CJD has been suggested on the basis of laboratory
studies but is unsupported by epidemiologic observation.
Such a link might yet be established by the discovery
of a specific molecular marker or of particular combinations
of trends over time of typical and atypical BSE and various
subtypes of sporadic CJD, as their numbers are influenced
by a continuation of current public health measures that
exclude high-risk bovine tissues from the animal and
human food chains.
SNIP...
Sporadic CJD
The possibility that at least some cases of apparently sporadic CJD might be due to infection by sporadic cases of BSE cannot be dismissed outright. Screening programs needed to identify sporadic BSE have yet to be implemented, and we know from already extant testing programs that at least a proportion of infected animals have no symptoms and thus would never be identified in the absence of systematic testing. Thus, sporadic BSE (or for that matter, sporadic disease in any mammalian species) might be occurring on a regular basis at perhaps the same annual frequency as sporadic CJD in humans, that is, in the range of 1 case per million animals.
Whether humans might be more susceptible to atypical forms of BSE cannot be answered at this time. Experimentally transmitted BASE shows shorter incubation periods than BSE in at least 1 breed of cattle, bovinized transgenic mice, and Cynomolgus monkeys (12,13). In humanized transgenic mice, BASE transmitted, whereas typical BSE did not transmit (13). Paradoxically, the other major phenotype (H) showed an unusually long incubation period in bovinized transgenic mice (12).
The limited experimental evidence bearing on a possible relationship between BSE and sporadic CJD is difficult to interpret. The original atypical BASE strain of BSE had a molecular protein signature very similar to that of 1 subtype (type 2 M/V) of sporadic CJD in humans (5). In another study, a strain of typical BSE injected into humanized mice encoding valine at codon 129 showed a glycopattern indistinguishable from the same subtype of sporadic CJD (15). In a third study, the glycopatterns of both the H and L strains of atypical BSE evidently did not resemble any of the known sporadic CJD subtypes (12).
To these molecular biology observations can be added the epidemiologic data accumulated during the past 30 years. The hypothesis that at least some cases of apparently sporadic CJD are due to unrecognized BSE infections cannot be formally refuted, but if correct, we might expect by now to have some epidemiologic evidence linking BSE to at least 1 cluster of apparently sporadic cases of CJD. Although only a few clusters have been found (and still fewer published), every proposed cluster that has been investigated has failed to show any common exposure to bovines. For that matter, no common exposure has been shown to any environmental vehicles of infection, including the consumption of foodstuffs from bovine, ovine, and porcine sources, the 3 livestock species known to be susceptible to transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Additional negative evidence comes from several large case-control studies in which no statistically significant dietary differences were observed between patients with sporadic CJD and controls (16,17).
On the other hand, the difficulty of establishing a link between BSE and CJD may be compounded by our ignorance of the infectious parameters of a sporadic form of BSE (e.g., host range, tissue distribution of infectivity, route of transmission, minimum infectious dose for humans, whether single or multiple). Presumably, these parameters would resemble those of variant CJD; that is, high infectivity central nervous system and lymphoreticular tissues of an infected cow find their way into products consumed by humans. Transmissions that might have occurred in the past would be difficult to detect because meat products are generally not distributed in a way that results in detectable geographic clusters.
Barring the discovery of a specific molecular signature (as in variant CJD), the most convincing clue to an association will come from the observation of trends over time of the incidence of typical and atypical BSE and of sporadic and variant CJD. With 4 diseases, each of which could have increasing, unchanging, or decreasing trends, there could be 81 (34) possible different combinations. However, it is highly likely that the trends for typical BSE and variant CJD will both decrease in parallel as feed bans continue to interrupt recycled contamination. The remaining combinations are thus reduced to 9 (32), and some of them could be highly informative.
For example, if the incidence of atypical BSE declines in parallel with that of typical BSE, its candidacy as a sporadic form of disease would be eliminated (because sporadic disease would not be influenced by current measures to prevent oral infection). If, on the other hand, atypical BSE continues to occur as typical BSE disappears, this would be a strong indication that it is indeed sporadic, and if in addition at least 1 form of what is presently considered as sporadic CJD (such as the type 2 M/V subtype shown to have a Western blot signature like BASE) were to increase, this would suggest (although not prove) a causal relationship (Figure 5).
Recognition of the different forms of BSE and CJD depends upon continuing systematic testing for both bovines and humans, but bovine testing will be vulnerable to heavy pressure from industry to dismantle the program as the commercial impact of declining BSE cases ceases to be an issue. Industry should be aware, however, of the implications of sporadic BSE. Its occurrence would necessitate the indefinite retention of all of the public health measures that exclude high-risk bovine tissues from the animal and human food chains, whereas its nonoccurrence would permit tissues that are now destroyed to be used as before, once orally acquired BSE has disappeared.
SNIP...
PLEASE READ FULL TEXT ;
http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/EID/vol12no12/06-0965.htm?s_cid=eid06_0965_e
3:00 Afternoon Refreshment Break, Poster and Exhibit Viewing in the Exhibit
Hall
3:30 Transmission of the Italian Atypical BSE (BASE) in Humanized Mouse
Models Qingzhong Kong, Ph.D., Assistant Professor, Pathology, Case Western Reserve
University
Bovine Amyloid Spongiform Encephalopathy (BASE) is an atypical BSE strain
discovered recently in Italy, and similar or different atypical BSE cases
were also reported in other countries. The infectivity and phenotypes of
these atypical BSE strains in humans are unknown. In collaboration with
Pierluigi Gambetti, as well as Maria Caramelli and her co-workers, we have
inoculated transgenic mice expressing human prion protein with brain
homogenates from BASE or BSE infected cattle. Our data shows that about half
of the BASE-inoculated mice became infected with an average incubation time
of about 19 months; in contrast, none of the BSE-inoculated mice appear to
be infected after more than 2 years. ***These results indicate that BASE is
transmissible to humans and suggest that BASE is more virulent than
classical BSE in humans.
6:30 Close of Day One
http://www.healthtech.com/2007/tse/day1.asp
SEE STEADY INCREASE IN SPORADIC CJD IN THE USA FROM
1997 TO 2006. SPORADIC CJD CASES TRIPLED, with phenotype
of 'UNKNOWN' strain growing. ...
http://www.cjdsurveillance.com/resources-casereport.html
There is a growing number of human CJD cases, and they were presented last
week in San Francisco by Luigi Gambatti(?) from his CJD surveillance
collection.
He estimates that it may be up to 14 or 15 persons which display selectively
SPRPSC and practically no detected RPRPSC proteins.
http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/06/transcripts/1006-4240t1.htm
http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/06/transcripts/2006-4240t1.pdf
JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY
MARCH 26, 2003
RE-Monitoring the occurrence of emerging forms of Creutzfeldt-Jakob
disease in the United States
Email Terry S. Singeltary:
flounder@wt.net
I lost my mother to hvCJD (Heidenhain Variant CJD). I would like to
comment on the CDC's attempts to monitor the occurrence of emerging
forms of CJD. Asante, Collinge et al [1] have reported that BSE
transmission to the 129-methionine genotype can lead to an alternate
phenotype that is indistinguishable from type 2 PrPSc, the commonest
sporadic CJD. However, CJD and all human TSEs are not reportable
nationally. CJD and all human TSEs must be made reportable in every
state and internationally. I hope that the CDC does not continue to
expect us to still believe that the 85%+ of all CJD cases which are
sporadic are all spontaneous, without route/source. We have many TSEs in
the USA in both animal and man. CWD in deer/elk is spreading rapidly and
CWD does transmit to mink, ferret, cattle, and squirrel monkey by
intracerebral inoculation. With the known incubation periods in other
TSEs, oral transmission studies of CWD may take much longer. Every
victim/family of CJD/TSEs should be asked about route and source of this
agent. To prolong this will only spread the agent and needlessly expose
others. In light of the findings of Asante and Collinge et al, there
should be drastic measures to safeguard the medical and surgical arena
from sporadic CJDs and all human TSEs. I only ponder how many sporadic
CJDs in the USA are type 2 PrPSc?
http://www.neurology.org/cgi/eletters/60/2/176#535
Diagnosis and Reporting of Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
Singeltary, Sr et al. JAMA.2001; 285: 733-734.
http://jama.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/full/285/6/733?maxtoshow=&HITS=10&hits=10&RESULTFORMAT=&fulltext=dignosing+and+reporting+creutzfeldt+jakob+disease&searchid=1048865596978_1528&stored_search=&FIRSTINDEX=0&journalcode=jama
BRITISH MEDICAL JOURNAL
BMJ
http://www.bmj.com/cgi/eletters/319/7220/1312/b#EL2
BMJ
http://www.bmj.com/cgi/eletters/320/7226/8/b#EL1
[Docket No. 03-025IFA] FSIS Prohibition of the Use of Specified Risk
Materials for Human Food and Requirement for the Disposition of
Non-Ambulatory Disabled Cattle
http://www.fsis.usda.gov/OPPDE/Comments/03-025IFA/03-025IFA-2.pdf
[Docket No. FSIS-2006-0011] FSIS Harvard Risk Assessment of Bovine
Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE)
http://www.fsis.usda.gov/OPPDE/Comments/2006-0011/2006-0011-1.pdf
THE SEVEN SCIENTIST REPORT ***
http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/dockets/02n0273/02n-0273-EC244-Attach-1.pdf
PAUL BROWN M.D.
http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/dockets/02n0273/02n-0273-c000490-vol40.pdf
9 December 2005
Division of Dockets Management (RFA-305)
SEROLOGICALS CORPORATION
James J. Kramer, Ph.D.
Vice President, Corporate Operations
http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/dockets/02n0273/02n-0273-c000383-01-vol35.pdf
Embassy of Japan
http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/dockets/02n0273/02N-0273-EC240.htm
Dockets Entered on December 22, 2005
2005D-0330, Guidance for Industry and FDA Review Staff on Collection of
Platelets
by Automated ... EC 203, McDonald's Restaurants Corporation, Vol #:, 34 ...
http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/dailys/05/Dec05/122205/122205.htm
03-025IF 03-025IF-631 Linda A. Detwiler [PDF]
Page 1. 03-025IF 03-025IF-631 Linda A. Detwiler Page 2. Page 3. Page 4.
Page 5. Page 6. Page 7. Page 8. Page 9. Page 10. Page 11. Page 12.
http://www.fsis.usda.gov/OPPDE/Comments/03-025IF/03-025IF-631.pdf
03-025IF 03-025IF-634 Linda A. Detwiler [PDF]
Page 1. 03-025IF 03-025IF-634 Linda A. Detwiler Page 2.
Page 3. Page 4. Page 5. Page 6. Page 7. Page 8.
http://www.fsis.usda.gov/OPPDE/Comments/03-025IF/03-025IF-634.pdf
Page 1 of 17 9/13/2005 [PDF]
... 2005 6:17 PM To: fsis.regulationscomments@fsis.usda.gov Subject: [Docket
No. 03-025IFA]
FSIS Prohibition of the Use of Specified Risk Materials for Human Food ...
http://www.fsis.usda.gov/OPPDE/Comments/03-025IFA/03-025IFA-2.pdf
03-025IFA 03-025IFA-6 Jason Frost [PDF]
... Zealand Embassy COMMENTS ON FEDERAL REGISTER 9 CFR Parts 309 et al
[Docket No. 03-
025IF] Prohibition of the Use of Specified Risk Materials for Human Food and
...
http://www.fsis.usda.gov/OPPDE/Comments/03-025IFA/03-025IFA-6.pdf
In its opinion of 7-8 December 2000 (EC 2000), the SSC ... [PDF]
Page 1. Linda A. Detwiler, DVM 225 Hwy 35 Red Bank, New Jersey 07701 Phone:
732-741-2290
Cell: 732-580-9391 Fax: 732-741-7751 June 22, 2005 FSIS Docket Clerk US ...
http://www.fsis.usda.gov/OPPDE/Comments/03-025IF/03-025IF-589.pdf
##################### Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy #####################
Subject: MAD COW FDA FEED WARNING LETTER NO. 2007-NOL-01 October 26, 2006 H.J. Baker & Bro., Inc.
Date: November 7, 2006 at 9:08 am PST
Food and Drug Administration
New Orleans District
404 BNA Drive, Building 200, Suite 500
Nashville, TN 37217
Telephone: 615-366-7801
Facsimile: 615-366-7802
October 26, 2006
WARNING LETTER NO. 2007-NOL-01
FEDERAL EXPRESS
OVERNIGHT DELIVERY
Mr. Christopher V. B. Smith
Corporate President, CEO
H. J. Baker & Bro., Inc.
228 Saugatuck Avenue
Westport, Connecticut 06880
Dear Mr. Smith:
On June 6, 8, 12-15, and 23, 2006, a U.S . Food and Drug Administration (FDA) investigator inspected
your animal feed protein supplement manufacturing facility, located at 603 Railroad Avenue,
Albertville, Alabama. The inspection revealed significant deviations from the requirements set forth in
Title 21, Code ofFederal Regulations, Part 589.2000 (21 CFR 589.2000), Animal Proteins Prohibited in
Ruminant Feed. This regulation is intended to prevent the establishment and amplification of Bovine
Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE). You failed to follow the requirements of this regulation, resulting
in products being manufactured and distributed by your facility because they are adulterated within the
meaning of Section 402(a)(4) [21 USC 342(a)(4)] of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (the
Act) and misbranded within the meaning of Section 403(a)(1) [21 USC 343(a)(1)] of the Act.
Our investigation determined adulteration resulted from the failure of your firm to establish and
implement measures sufficient to prevent commingling or cross-contamination . The adulterated feed
was subsequently misbranded because it was not properly labeled. Specifically, we found :
" Your firm failed to establish and use cleanout procedures or other means to prevent carry-over of
products which contain or may contain protein derived from mammalian tissues into animal protein
or feeds which may be used for ruminants, as required by 21 CFR 589.2000(e)(1)(iii)(B) .
Specifically, you failed to establish and use such measures for a screw auger installed in February
2005 . This auger is used to convey both prohibited and non-prohibited material to bulk storage bins.
In addition, you failed to follow the cleanout procedure your firm had developed for the receiving
systems. Your feed is, therefore, adulterated under Section 402(a)(4) [21 USC 342(a)(4)] of the Act.
" You failed to label all products which contained or may have contained prohibited materials with the
BSE cautionary statement, "Do not feed to cattle or other ruminants," as required by 21 CFR
589.2000(e)(1)(i) . Such products are misbranded under Section 403(3) [21 USC 343(a)(1)] of the
Act. These misbranded products include the three Pro-Pak products mentioned below, as well as
Page 2 - H. J . Baker & Bro., Inc., Albertville, Alabama Warning Letter No. 2007-NOL-O 1
those bulk loads of individual feed ingredients processed through this common screw auger and
distributed between the time it was installed in February 2005, and June 9, 2006 .
This letter is not intended to serve as an all-inclusive list of violations at your facility. As a
manufacturer of materials intended for animal feed use, you are responsible for ensuring your overall
operation and the products you manufacture and distribute are in compliance with the law. You should take prompt action to correct these violations, and you should establish a system whereby violations do not recur. Failure to promptly correct these violations may result in regulatory action, such as seizure and/or injunction, without further notice.
We acknowledge your June 16, 2006, voluntary recall of three products you manufactured from
February 2005 to June 2006. The three products recalled were: Pro-Lak Protein Concentrate for
Lactating Dairy Animals; Pro-Amino II for PreFresh and Lactating Cows; and, Pro-Pak Marine & Animal Protein Concentrate for Use in Animal Feed. Recall effectiveness checks and other measures
will determine the merit of this recall . We recognize you now label all products with the required BSE
cautionary statement and we also acknowledge your intent, given verbally to New Orleans District
management of the FDA, to discontinue the production of supplements which do not contain prohibited
materials. In your written response to this letter, please confirm in writing you have taken these steps.
You should notify this office in writing within 15 working days of receiving this letter, outlining the specific steps you have taken to bring your firm into compliance with the law, including the steps we acknowledge above and any additional steps you have taken. Your response should include an
explanation of each step taken to correct the violations and prevent their recurrence. If corrective action cannot be completed within 15 working days, state the reason for the delay and the date by which the corrections will be completed. Include copies of any available documentation demonstrating corrections have been made.
Your reply should be directed to Kari L. Batey, Compliance Officer, at the address above. If you have
questions regarding any issue in this letter, please contact Ms. Batey at (615) 366-7808.
Sincerely,
,
Carol S . Sanchez
Acting District Director
New Orleans District
Enclosure: Form FDA 483
cc: Craig R. Waterhouse
Plant Manager
H.J. Baker & Bros., Inc.
603 Railroad Avenue
Albertville, Alabama 35951-3419
http://www.fda.gov/foi/warning_letters/g6104d.pdf
TSS
MORE 2006 FEED BAN VIOLATIONS BELOW, ''IN COMMERCE'' ;
Subject: MAD COW FEED RECALL USA SEPT 6, 2006 1961.72 TONS IN COMMERCE AL,
TN, AND WV
Date: September 6, 2006 at 7:58 am PST
PRODUCT
a) EVSRC Custom dairy feed, Recall # V-130-6;
b) Performance Chick Starter, Recall # V-131-6;
c) Performance Quail Grower, Recall # V-132-6;
d) Performance Pheasant Finisher, Recall # V-133-6.
CODE
None
RECALLING FIRM/MANUFACTURER
Donaldson & Hasenbein/dba J&R Feed Service, Inc., Cullman, AL, by telephone
on June 23, 2006 and by letter dated July 19, 2006. Firm initiated recall is
complete.
REASON
Dairy and poultry feeds were possibly contaminated with ruminant based
protein.
VOLUME OF PRODUCT IN COMMERCE
477.72 tons
DISTRIBUTION
AL
______________________________
PRODUCT
a) Dairy feed, custom, Recall # V-134-6;
b) Custom Dairy Feed with Monensin, Recall # V-135-6.
CODE
None. Bulk product
RECALLING FIRM/MANUFACTURER
Recalling Firm: Burkmann Feed, Greeneville, TN, by Telephone beginning on
June 28, 2006.
Manufacturer: H. J. Baker & Bro., Inc., Albertville, AL. Firm initiated
recall is complete.
REASON
Possible contamination of dairy feeds with ruminant derived meat and bone
meal.
VOLUME OF PRODUCT IN COMMERCE
1,484 tons
DISTRIBUTION
TN and WV
http://www.fda.gov/bbs/topics/enforce/2006/ENF00968.html
Subject: MAD COW FEED RECALLS ENFORCEMENT REPORT FOR AUGUST 9, 2006 KY, LA,
MS, AL, GA, AND TN 11,000+ TONS
Date: August 16, 2006 at 9:19 am PST
RECALLS AND FIELD CORRECTIONS: VETERINARY MEDICINE - CLASS II
______________________________
PRODUCT
Bulk custom made dairy feed, Recall # V-115-6
CODE
None
RECALLING FIRM/MANUFACTURER
Hiseville Feed & Seed Co., Hiseville, KY, by telephone and letter on or
about July 14, 2006. FDA initiated recall is ongoing.
REASON
Custom made feeds contain ingredient called Pro-Lak which may contain
ruminant derived meat and bone meal.
VOLUME OF PRODUCT IN COMMERCE
Approximately 2,223 tons
DISTRIBUTION
KY
______________________________
PRODUCT
Bulk custom made dairy feed, Recall # V-116-6
CODE
None
RECALLING FIRM/MANUFACTURER
Rips Farm Center, Tollesboro, KY, by telephone and letter on July 14, 2006.
FDA initiated recall is ongoing.
REASON
Custom made feeds contain ingredient called Pro-Lak which may contain
ruminant derived meat and bone meal.
VOLUME OF PRODUCT IN COMMERCE
1,220 tons
DISTRIBUTION
KY
______________________________
PRODUCT
Bulk custom made dairy feed, Recall # V-117-6
CODE
None
RECALLING FIRM/MANUFACTURER
Kentwood Co-op, Kentwood, LA, by telephone on June 27, 2006. FDA initiated
recall is completed.
REASON
Possible contamination of animal feed ingredients, including ingredients
that are used in feed for dairy animals, with ruminant derived meat and bone
meal.
VOLUME OF PRODUCT IN COMMERCE
40 tons
DISTRIBUTION
LA and MS
______________________________
PRODUCT
Bulk Dairy Feed, Recall V-118-6
CODE
None
RECALLING FIRM/MANUFACTURER
Cal Maine Foods, Inc., Edwards, MS, by telephone on June 26, 2006. FDA
initiated recall is complete.
REASON
Possible contamination of animal feed ingredients, including ingredients
that are used in feed for dairy animals, with ruminant derived meat and bone
meal.
VOLUME OF PRODUCT IN COMMERCE
7,150 tons
DISTRIBUTION
MS
______________________________
PRODUCT
Bulk custom dairy pre-mixes, Recall # V-119-6
CODE
None
RECALLING FIRM/MANUFACTURER
Walthall County Co-op, Tylertown, MS, by telephone on June 26, 2006. Firm
initiated recall is complete.
REASON
Possible contamination of dairy animal feeds with ruminant derived meat and
bone meal.
VOLUME OF PRODUCT IN COMMERCE
87 tons
DISTRIBUTION
MS
______________________________
PRODUCT
Bulk custom dairy pre-mixes, Recall # V-120-6
CODE
None
RECALLING FIRM/MANUFACTURER
Ware Milling Inc., Houston, MS, by telephone on June 23, 2006. Firm
initiated recall is complete.
REASON
Possible contamination of dairy animal feeds with ruminant derived meat and
bone meal.
VOLUME OF PRODUCT IN COMMERCE
350 tons
DISTRIBUTION
AL and MS
______________________________
PRODUCT
a) Tucker Milling, LLC Tm 32% Sinking Fish Grower, #2680-Pellet,
50 lb. bags, Recall # V-121-6;
b) Tucker Milling, LLC #31120, Game Bird Breeder Pellet,
50 lb. bags, Recall # V-122-6;
c) Tucker Milling, LLC #31232 Game Bird Grower,
50 lb. bags, Recall # V-123-6;
d) Tucker Milling, LLC 31227-Crumble, Game Bird Starter, BMD
Medicated, 50 lb bags, Recall # V-124-6;
e) Tucker Milling, LLC #31120, Game Bird Breeder, 50 lb bags,
Recall # V-125-6;
f) Tucker Milling, LLC #30230, 30 % Turkey Starter, 50 lb bags,
Recall # V-126-6;
g) Tucker Milling, LLC #30116, TM Broiler Finisher,
50 lb bags, Recall # V-127-6
CODE
All products manufactured from 02/01/2005 until 06/20/2006
RECALLING FIRM/MANUFACTURER
Recalling Firm: Tucker Milling LLC, Guntersville, AL, by telephone and visit
on June 20, 2006, and by letter on June 23, 2006.
Manufacturer: H. J. Baker and Brothers Inc., Stamford, CT. Firm initiated
recall is ongoing.
REASON
Poultry and fish feeds which were possibly contaminated with ruminant based
protein were not labeled as "Do not feed to ruminants".
VOLUME OF PRODUCT IN COMMERCE
7,541-50 lb bags
DISTRIBUTION
AL, GA, MS, and TN
END OF ENFORCEMENT REPORT FOR AUGUST 9, 2006
###
http://www.fda.gov/bbs/topics/ENFORCE/2006/ENF00964.html
Subject: MAD COW FEED RECALL MI MAMMALIAN PROTEIN VOLUME OF PRODUCT IN
COMMERCE 27,694,240 lbs
Date: August 6, 2006 at 6:14 pm PST
PRODUCT
Bulk custom dairy feds manufactured from concentrates, Recall # V-113-6
CODE
All dairy feeds produced between 2/1/05 and 6/16/06 and containing H. J.
Baker recalled feed products.
RECALLING FIRM/MANUFACTURER
Vita Plus Corp., Gagetown, MI, by visit beginning on June 21, 2006. Firm
initiated recall is complete.
REASON
The feed was manufactured from materials that may have been contaminated
with mammalian protein.
VOLUME OF PRODUCT IN COMMERCE
27,694,240 lbs
DISTRIBUTION
MI
END OF ENFORCEMENT REPORT FOR AUGUST 2, 2006
###
http://www.fda.gov/bbs/topics/enforce/2006/ENF00963.html
Subject: MAD COW FEED RECALL AL AND FL VOLUME OF PRODUCT IN COMMERCE 125
TONS Products manufactured from 02/01/2005 until 06/06/2006
Date: August 6, 2006 at 6:16 pm PST
PRODUCT
a) CO-OP 32% Sinking Catfish, Recall # V-100-6;
b) Performance Sheep Pell W/Decox/A/N, medicated,
net wt. 50 lbs, Recall # V-101-6;
c) Pro 40% Swine Conc Meal -- 50 lb, Recall # V-102-6;
d) CO-OP 32% Sinking Catfish Food Medicated,
Recall # V-103-6;
e) "Big Jim's" BBB Deer Ration, Big Buck Blend,
Recall # V-104-6;
f) CO-OP 40% Hog Supplement Medicated Pelleted,
Tylosin 100 grams/ton, 50 lb. bag, Recall # V-105-6;
g) Pig Starter Pell II, 18% W/MCDX Medicated 282020,
Carbadox -- 0.0055%, Recall # V-106-6;
h) CO-OP STARTER-GROWER CRUMBLES, Complete
Feed for Chickens from Hatch to 20 Weeks, Medicated,
Bacitracin Methylene Disalicylate, 25 and 50 Lbs,
Recall # V-107-6;
i) CO-OP LAYING PELLETS, Complete Feed for Laying
Chickens, Recall # 108-6;
j) CO-OP LAYING CRUMBLES, Recall # V-109-6;
k) CO-OP QUAIL FLIGHT CONDITIONER MEDICATED,
net wt 50 Lbs, Recall # V-110-6;
l) CO-OP QUAIL STARTER MEDICATED, Net Wt. 50 Lbs,
Recall # V-111-6;
m) CO-OP QUAIL GROWER MEDICATED, 50 Lbs,
Recall # V-112-6
CODE
Product manufactured from 02/01/2005 until 06/06/2006
RECALLING FIRM/MANUFACTURER
Alabama Farmers Cooperative, Inc., Decatur, AL, by telephone, fax, email and
visit on June 9, 2006. FDA initiated recall is complete.
REASON
Animal and fish feeds which were possibly contaminated with ruminant based
protein not labeled as "Do not feed to ruminants".
VOLUME OF PRODUCT IN COMMERCE
125 tons
DISTRIBUTION
AL and FL
END OF ENFORCEMENT REPORT FOR AUGUST 2, 2006
###
http://www.fda.gov/bbs/topics/enforce/2006/ENF00963.html
Subject: MAD COW FEED RECALL KY VOLUME OF PRODUCT IN COMMERCE ?????
Date: August 6, 2006 at 6:19 pm PST
PRODUCT
Bulk custom made dairy feed, Recall # V-114-6
CODE
None
RECALLING FIRM/MANUFACTURER
Burkmann Feeds LLC, Glasgow, KY, by letter on July 14, 2006. Firm initiated
recall is ongoing.
REASON
Custom made feeds contain ingredient called Pro-Lak, which may contain
ruminant derived meat and bone meal.
VOLUME OF PRODUCT IN COMMERCE
?????
DISTRIBUTION
KY
END OF ENFORCEMENT REPORT FOR AUGUST 2, 2006
###
http://www.fda.gov/bbs/topics/enforce/2006/ENF00963.html
CJD WATCH MESSAGE BOARD
TSS
MAD COW FEED RECALL USA EQUALS 10,878.06 TONS NATIONWIDE
Sun Jul 16, 2006 09:22
71.248.128.67
RECALLS AND FIELD CORRECTIONS: VETERINARY MEDICINE -- CLASS II
______________________________
PRODUCT
a) PRO-LAK, bulk weight, Protein Concentrate for Lactating Dairy Animals,
Recall # V-079-6;
b) ProAmino II, FOR PREFRESH AND LACTATING COWS, net weight 50lb (22.6 kg),
Recall # V-080-6;
c) PRO-PAK, MARINE & ANIMAL PROTEIN CONCENTRATE FOR USE IN ANIMAL
FEED, Recall # V-081-6;
d) Feather Meal, Recall # V-082-6
CODE
a) Bulk
b) None
c) Bulk
d) Bulk
RECALLING FIRM/MANUFACTURER
H. J. Baker & Bro., Inc., Albertville, AL, by telephone on June 15, 2006 and
by press release on June 16, 2006. Firm initiated recall is ongoing.
REASON
Possible contamination of animal feeds with ruminent derived meat and bone
meal.
VOLUME OF PRODUCT IN COMMERCE
10,878.06 tons
DISTRIBUTION
Nationwide
END OF ENFORCEMENT REPORT FOR July 12, 2006
###
http://www.fda.gov/bbs/topics/enforce/2006/ENF00960.html
Subject: MAD COW FEED BAN WARNING LETTER ISSUED MAY 17, 2006
Date: June 27, 2006 at 7:42 am PST
Public Health Service
Food and Drug Administration
New Orleans District
297 Plus Park Blvd.
Nashville, TN 37217
Telephone: 615-781-5380
Fax: 615-781-5391
May 17, 2006
WARNING LETTER NO. 2006-NOL-06
FEDERAL EXPRESS
OVERNIGHT DELIVERY
Mr. William Shirley, Jr., Owner
Louisiana.DBA Riegel By-Products
2621 State Street
Dallas, Texas 75204
Dear Mr. Shirley:
On February 12, 17, 21, and 22, 2006, a U.S. Food & Drug Administration
(FDA) investigator inspected your rendering plant, located at 509 Fortson
Street, Shreveport, Louisiana. The inspection revealed significant
deviations from the requirements set forth in Title 21, Code of Federal
Regulations, Part 589.2000 [21 CFR 589.2000], Animal Proteins Prohibited in
Ruminant Feed. This regulation is intended to prevent the establishment and
amplification of Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE). You failed to
follow the requirements of this regulation; products being manufactured and
distributed by your facility are misbranded within the meaning of Section
403(a)(1) [21 USC 343(a)(1)] of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act
(the Act).
Our investigation found you failed to provide measures, including sufficient
written procedures, to prevent commingling or cross-contamination and to
maintain sufficient written procedures [21 CFR 589.2000(e)] because:
You failed to use clean-out procedures or other means adequate to prevent
carryover of protein derived from mammalian tissues into animal protein or
feeds which may be used for ruminants. For example, your facility uses the
same equipment to process mammalian and poultry tissues. However, you use
only hot water to clean the cookers between processing tissues from each
species. You do not clean the auger, hammer mill, grinder, and spouts after
processing mammalian tissues.
You failed to maintain written procedures specifying the clean-out
procedures or other means to prevent carryover of protein derived from
mammalian tissues into feeds which may be used for ruminants.
As a result . the poultry meal you manufacture may contain protein derived
from mammalian tissues prohibited in ruminant feed. Pursuant to 21 CFR
589.2000(e)(1)(i), any products containing or may contain protein derived
from mammalian tissues must be labeled, "Do not feed to cattle or other
ruminants." Since you failed to label a product which may contain protein
derived from mammalian tissues with the required cautionary statement. the
poultry meal is misbranded under Section 403(a)(1) [21 USC 343(a)(1)] of the
Act.
This letter is not intended as an all-inclusive list of violations at your
facility. As a manufacturer of materials intended for animal feed use, you
are responsible for ensuring your overall operation and the products you
manufacture and distribute are in compliance with the law. You should take
prompt action to correct these violations, and you should establish a system
whereby violations do not recur. Failure to promptly correct these
violations may result in regulatory action, such as seizure and/or
injunction, without further notice.
You should notify this office in writing within 15 working days of receiving
this letter, outlining the specific steps you have taken to bring your firm
into compliance with the law. Your response should include an explanation of
each step taken to correct the violations and prevent their recurrence. If
corrective action cannot be completed within 15 working days, state the
reason for the delay and the date by which the corrections will be
completed. Include copies of any available documentation demonstrating
corrections have been made.
Your reply should be directed to Mark W. Rivero, Compliance Officer, U.S.
Food and Drug Administration, 2424 Edenborn Avenue, Suite 410, Metairie,
Louisiana 70001. If you have questions regarding any issue in this letter,
please contact Mr. Rivero at (504) 219-8818, extension 103.
Sincerely,
/S
Carol S. Sanchez
Acting District Director
New Orleans District
http://www.fda.gov/foi/warning_letters/g5883d.htm
look at the table and you'll see that as little as 1 mg (or 0.001 gm) caused
7% (1 of 14) of the cows to come down with BSE;
Risk of oral infection with bovine spongiform encephalopathy agent in
primates
Corinne Ida Lasmézas, Emmanuel Comoy, Stephen Hawkins, Christian Herzog,
Franck Mouthon, Timm Konold, Frédéric Auvré, Evelyne Correia, Nathalie
Lescoutra-Etchegaray, Nicole Salès, Gerald Wells, Paul Brown, Jean-Philippe
Deslys
Summary The uncertain extent of human exposure to bovine spongiform
encephalopathy (BSE)--which can lead to variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
(vCJD)--is compounded by incomplete knowledge about the efficiency of oral
infection and the magnitude of any bovine-to-human biological barrier to
transmission. We therefore investigated oral transmission of BSE to
non-human primates. We gave two macaques a 5 g oral dose of brain homogenate
from a BSE-infected cow. One macaque developed vCJD-like neurological
disease 60 months after exposure, whereas the other remained free of disease
at 76 months. On the basis of these findings and data from other studies, we
made a preliminary estimate of the food exposure risk for man, which
provides additional assurance that existing public health measures can
prevent transmission of BSE to man.
snip...
BSE bovine brain inoculum
100 g 10 g 5 g 1 g 100 mg 10 mg 1 mg 0·1 mg 0·01 mg
Primate (oral route)* 1/2 (50%)
Cattle (oral route)* 10/10 (100%) 7/9 (78%) 7/10 (70%) 3/15 (20%) 1/15 (7%)
1/15 (7%)
RIII mice (ic ip route)* 17/18 (94%) 15/17 (88%) 1/14 (7%)
PrPres biochemical detection
The comparison is made on the basis of calibration of the bovine inoculum
used in our study with primates against a bovine brain inoculum with a
similar PrPres concentration that was
inoculated into mice and cattle.8 *Data are number of animals
positive/number of animals surviving at the time of clinical onset of
disease in the first positive animal (%). The accuracy of
bioassays is generally judged to be about plus or minus 1 log. ic
ip=intracerebral and intraperitoneal.
Table 1: Comparison of transmission rates in primates and cattle infected
orally with similar BSE brain inocula
Published online January 27, 2005
http://www.thelancet.com/journal/journal.isa
It is clear that the designing scientists must
also have shared Mr Bradley's surprise at the results because all the dose
levels right down to 1 gram triggered infection.
http://www.bseinquiry.gov.uk/files/ws/s145d.pdf
2
6. It also appears to me that Mr Bradley's answer (that it would take less
than say 100
grams) was probably given with the benefit of hindsight; particularly if one
considers that later in the same answer Mr Bradley expresses his surprise
that it
could take as little of 1 gram of brain to cause BSE by the oral route
within the
same species. This information did not become available until the "attack
rate"
experiment had been completed in 1995/96. This was a titration experiment
designed to ascertain the infective dose. A range of dosages was used to
ensure
that the actual result was within both a lower and an upper limit within the
study
and the designing scientists would not have expected all the dose levels to
trigger
infection. The dose ranges chosen by the most informed scientists at that
time
ranged from 1 gram to three times one hundred grams. It is clear that the
designing
scientists must have also shared Mr Bradley's surprise at the results
because all the
dose levels right down to 1 gram triggered infection.
http://www.bseinquiry.gov.uk/files/ws/s147f.pdf
Re: BSE .1 GRAM LETHAL NEW STUDY SAYS via W.H.O. Dr Maura Ricketts
[BBC radio 4 FARM news]
http://www.maddeer.org/audio/BBC4farmingtoday2_1_03.ram
http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/03/slides/3923s1_OPH.htm
2) Infectious dose:
To cattle: 1 gram of infected brain material (by oral ingestion)
http://www.inspection.gc.ca/english/sci/bio/bseesbe.shtml
TSS
#################### https://lists.aegee.org/bse-l.html ####################
Terry S. Singeltary SR.
P.O. Box 42
Bacliff, Texas USA 77518
Post a Comment
<< Home